-
4-minute read
-
29th August 2019
How to Cite Social Media in MLA Referencing
Social media is everywhere. Even referencing systems can’t ignore it anymore. As such, most now have rules for citing social media. Here, for example, we’re looking at how to cite Facebook and Twitter posts using MLA referencing, including both in-text citations and in the Works Cited list.
When to Cite Social Media in Academic Writing
Facebook and Twitter are not conventional academic sources. If you’re looking for a historical fact or a scientific theory, for example, you’re better off sticking to a book, ideally one written by a qualified professional.

However, it’s fine to cite a social media post if it’s relevant to your work. For example, you might need to cite social media if you’re writing about a company with a big online presence. And you may need to cite posts from different sites if you’re writing about social media itself.
If you do cite social media, however, make sure to do it right!
In-Text Citations for a Facebook or Twitter Post
When citing social media in MLA referencing, you won’t have any page numbers to work with. As such, citations should just identify the author. For a Facebook post, this means giving the surname of the poster or the account name. Usually, you can simply mention this in the text:
On Facebook, Julia Gillard promised “political support” for the scheme.
Here, for instance, we mention Julia Gillard’s Facebook page directly, so we don’t need a bracketed citation. But if you don’t mention the author or account in the text, you should give this detail in brackets:
The aim of this is to ensure “a quality education for all children” (Gillard).
With a tweet, meanwhile, you should cite the user’s Twitter handle in the citation rather than their surname. For example:
She said that the portraits “moved [her] beyond words” (@juliagillard).
The key, typically, is identifying the platform and account for the post cited.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Subscribe to Beyond the Margins and get your monthly fix of editorial strategy, workflow tips, and real-world examples from content leaders.
Social Media in the Works Cited List
In your Works Cited list, the format for a social media post is similar to other online sources. However, there are some specific requirements depending on the platform. With a Facebook post, the standard format is:
Surname, First Name or Account Name. “Excerpt from post.” Facebook, date posted, time posted, URL.
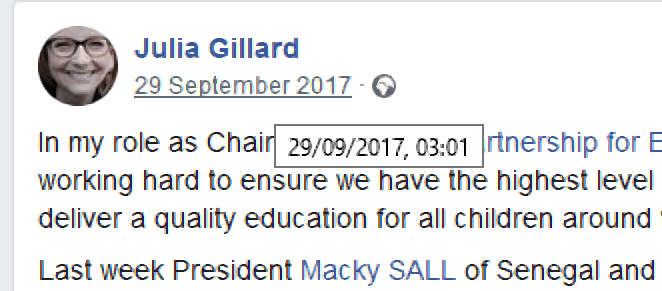
We use an excerpt here because Facebook posts don’t usually have a title. And while the time of a post won’t always be obvious, you can find it by hovering the cursor over the date on screen.
For a tweet, the standard format is similar, but you give the Twitter handle in first position, the name of the poster (if known) in brackets after, and the complete text of the tweet. For instance:
Twitter handle (Author Name). “Text of tweet.” Twitter, date posted, time posted, URL.
As such, we would list the posts used in the examples above as follows:
Gillard, Julia. “In my role as Chair of the Global Partnership for Education…” Facebook, 29 Sept. 2017, 3:01 p.m., www.facebook.com/juliagillard/posts/10155738538667328.
@juliagillard (Julia Gillard). “Vincent Fantauzzo’s portraits of Indigenous Australian artists moved me beyond words. Delighted he will be painting my official portrait. JG.” Twitter, 22 Sept. 2017, 3:56 p.m., twitter.com/JuliaGillard/status/911061529449005056.
We’ve shortened the names of months in these examples. This is standard in MLA, which abbreviates months in references if they’re more than four letters long. And if you’d like one of our MLA experts to check the referencing in your work, submit a document for proofreading today.




